RAD and Prototyping
RAD
- Rapid application development. Rapid application development offers a solution that enables systems to be developed much faster. They do this by using the following approaches:
- Use workshops and focus groups to gather requirements rather than a formal Requirement Document: The idea is to actively involve users for developing requirements rather than the analyst trying to collate everything to produce a Requirements Document.
- Use prototyping to refine the system with heavy involvement of the user
- Allocate strict time limits to develop each part of the system. The intent is to develop a system that is 'good enough' rather than one bloated with bells and whistles
- Re-use software components already to hand: Use software libraries that have well-developed, stable functions
Use object orientated programming methods to develop software classes, all parts of the system can then use these classes
Use a software application framework

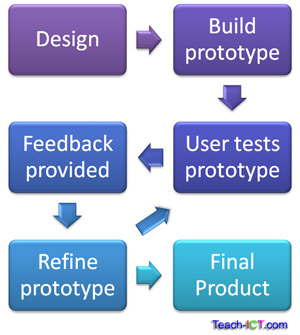
Prototyping
A prototype represents some aspect of the full system - for instance a mock-up of the graphical user interface. A prototype allows the end user to see what the end project will look like and how it will work before the developer spends a large amount of time on it, making sure that the project is going to meet the requirements.
A prototype is not a fully working system but it does provide an opportunity for the user to give feedback and suggestions for improvements. This may happen again and again until the full details are agreed between developer and user. Therefore prototyping is an 'iterative' process.
Any changes required are fed back to the developer and the Requirements Document is also updated every time a change is needed.
It is much cheaper to build a prototype and iron out the problems rather than go straight into the development of the main system and then find out there are problems
Evolutionary Prototyping
The idea behind this is that an initial prototype is presented to the user. They provide feedback and suggestions for improvements.
These are actioned by the developer who then presents a more refined prototype. The user once more provides feedback. The process is repeated.
So at each stage the prototype 'evolves' towards the final system.
Throwaway Prototyping
With 'throw-away' prototyping a small part of the system is developed and then given to the end user to try out and evaluate. The user provides feedback which can quickly be incorporated into the development of the main system.
The prototype is then discarded or thrown away,
The objective of throw-away prototyping is to ensure that the system requirements are validated and that they are clearly understood.
The throw-away prototype is NOT considered part of the final system. It is simply there to aid understanding and reduce the risk of poorly defined requirements. The full system is being developed alongside the prototypes and incorporates the changes needed.
Agile Development

Using prototyping and RAD over SDLC
The end user may not fully understand what the project being made is, therefore if a prototype was to be made it would help the end user to understand the project and make sure it will meet the requirements. Therefore prototyping would be beneficial on large projects over the SDLC in order to make sure that the developer does not spend large amounts of time and money on a project that the end user does not want. As well as this a working system is available early on in the process. The user can identify possible improvements which can be made before the system is completed, where as they will not get this opportunity if the developer uses the SDLC. Using prototyping and RAD will make the end user feel more involved in the project meaning they will 'buy' into it. The prototype will allow the end user to get a feel and use the system, reducing the amount of training that they will need if the developer was to use SDLC, It will also be much cheaper
Discuss the effectiveness of the System Development life cycle when designing mobile phone applications for a one person development company?
The System Development life cycle (SDLC) is a method of ICT development that could be used when designing mobile phone applications by a developer. The systems development life cycle is the process of stages which occur during the development of a new ICT system. The stages include; Definition; Investigation and analysis; Design; Implementation; Testing; Installation; Documentation; Evaluation and Maintenance.
The SDLC could be used by the developer to design mobile phone applications. It will allow the developer to break down the project into set easy to follow stages that the developer can work through. This will help the developer to make sure all of the necessary tasks needed for completing the mobile application will be met. The SDLC's systematic approach allows you to thoroughly plan for contingencies, risks, finances, resources, etc. It is a very phased approach with clear definitions between one phase and the next, allowing you to make a more structured plan with specific deadlines and deliverables. However If only one person is using the SDLC to design mobile applications it will be very time consuming, the developer will have follow all of the steps which can take time meaning the single developer may not be able to meet deadlines. As well as this if there is a problem with the phone application or a new mobile operating system for mobiles came out it would mean the application would need to be changed. To make amendments it would be very difficult, time consuming and expensive to do so if the single developer was using SDLC. Therefore I feel using prototyping may be more effective when designing mobile applications, this is because.
The SDLC could be used by the developer to design mobile phone applications. It will allow the developer to break down the project into set easy to follow stages that the developer can work through. This will help the developer to make sure all of the necessary tasks needed for completing the mobile application will be met. The SDLC's systematic approach allows you to thoroughly plan for contingencies, risks, finances, resources, etc. It is a very phased approach with clear definitions between one phase and the next, allowing you to make a more structured plan with specific deadlines and deliverables. However If only one person is using the SDLC to design mobile applications it will be very time consuming, the developer will have follow all of the steps which can take time meaning the single developer may not be able to meet deadlines. As well as this if there is a problem with the phone application or a new mobile operating system for mobiles came out it would mean the application would need to be changed. To make amendments it would be very difficult, time consuming and expensive to do so if the single developer was using SDLC. Therefore I feel using prototyping may be more effective when designing mobile applications, this is because.
No comments:
Post a Comment